6.5 Mixed Cropping
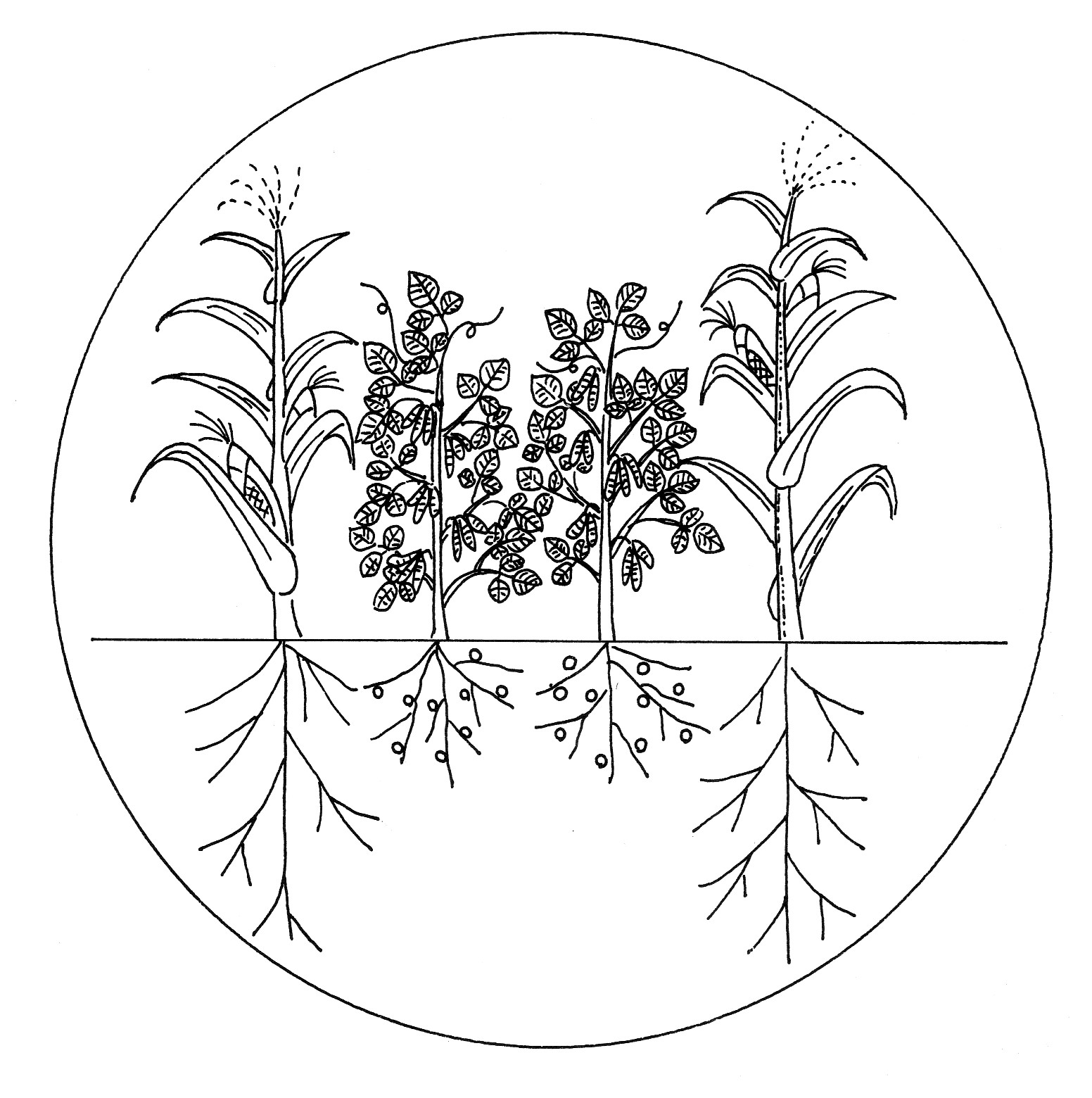
A mixed cropping system is a variation of diverse cropping and involves planting various kinds of crops together in a plot. For instance, planting maize with bean is found in many countries as a local farming practice. Maize (cereal crop) is tall, deep rooted and a high nutrient consuming crop while the bean is short, shallow rooted and a low nutrient consuming crop which also provides nitrogen to the soil. There is no competition between the maize and the bean and the maize can use nitrogen fixed by the bean. The total production of maize and bean together is higher than that of maize or bean alone. There are many other good combinations of plants like this.
The advantages of mixed cropping include decreasing pest problems, better use of land, sunlight and rainfall.
Factors to consider in plant combinations include:
Nutrient Consumption
As mentioned above, the combination of the cereal and the legume is appropriate in terms of the soil fertility maintenance. The cereal is a high nutrient consuming crop, while the legume is a low nutrient consuming crop which provides nitrogen to the soil by the N-fixing bacteria.
Root Depth
If a deep rooted crop is planted together with another deep rooted crop, both crops will compete with each other and not grow well. A shallow rooted crop with another shallow rooted crop causes more or less the same problem. The combination of a deep rooted crop and a shallow rooted crop is appropriate. Planting maize with pumpkin is a good example. The maize is the deep rooted crop and consumes nutrients in the sub soil (deeper zone). The pumpkin is the shallow rooted crop and consumes nutrients in shallow soil. There is less competition between the maize and the pumpkin. The deep rooted crop is usually a standing type of crop and the shallow rooted crop is generally spreading type crop.
Insect Repellent Plants
There are some crops which have a unique smell that repels some kinds of insects. For example, onion has a specific smell that butterflies dislike. If onion is planted with cabbage, the smell prevents the insects (worms) from attacking the cabbage. Combinations like onion and cabbage are called companion plants. The companion plant is very effective pest prevention measure.
Shade Tolerance
There are some crops which can grow well in the shade. The crops are called shade tolerant crops or shade loving crops. Planting shade tolerant crops under tree crops or tall crop plants increases the utilization of the land. Planting pineapple (Anarosh) under jack fruit (Katal) and ginger (Ada) under mango (Am) are some good examples.
Mixed Crop Combinations in Bangladesh
|
Main Crop
|
Companion Crops
|
| Mustard (Shorisha) |
Lentil, radish, grass pea (Khesari)
|
| Chili (Marich) |
Black gram (Mashkalai),radish, okra (Dherosh), egg plant
|
Cabbage (Bandakopi)
Cauliflower (Phulkopi) |
Onion (Piaj), tomato, coriander (Dhaniya), potato
|
| Maize (Dhuta) |
Ground nuts, Indian beans, lentil, mung beans (Mug), black gram, pumpkin (Mistikumra)
0
|
| Tomato |
Onion, garlic (Rashun), carrot (Gajar), cucumber (Shosha)
|
| Cucumber (Shosha) |
Radish, maize, beans (Dal), tomato
|
| Sugar cane (Ak) |
Lentil, ground nuts, grass peas
|
| Egg plant (Begun) |
Beans, chili, potato
|
| Potato (Alu) |
Beans, cabbage, peas (Matar), maize, egg plant
|
| Indian bean(Seem) |
Maize
|
| Ground nuts (Badam) |
Maize, sugar cane
|
| Radish (Mula) |
Cucumber, mustard, tomato, chili
|
| Lentil (Mashuri) |
Mustard, maize, sugar cane
|
|